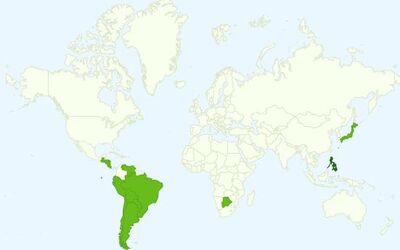
Countries and territories using ISDB-T
Asia
Americas
- Brazil
- Peru
- Argentina
- Chile
- Venezuela
- Ecuador
- Costa Rica
- Paraguay
- Bolivia
- Nicaragua
- Uruguay
- Guatemala
- Honduras
Africa
- Botswana
Features
ISDB-T is characterized by the following features:
- ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting-Terrestrial) in Japan use UHF 470 MHz-770 MHz
- bandwidth of 300 MHz, allocate 50 channels, namely channel 13 through to channel 62.
- 300 MHz with 50 channels. each channel is 6 MHz width (actually 5.572 MHz effective bandwidth and 430 kHz guard band between channels). These channels are called "physical channel".
- for other countries, US channel table or European channel table are used.
- Channel tables
- 6 MHz channel, channel bandwidth is 5.572 MHz.
- 7 MHz channel, channel bandwidth is 6.50 MHz.
- 8 MHz channel, channel bandwidth is 7.42 MHz.
- ISDB-T allows to accommodate any combination of:
- HDTV (roughly 8Mbit/s in H.264)
- SDTV (roughly 2Mbit/s in H.264)
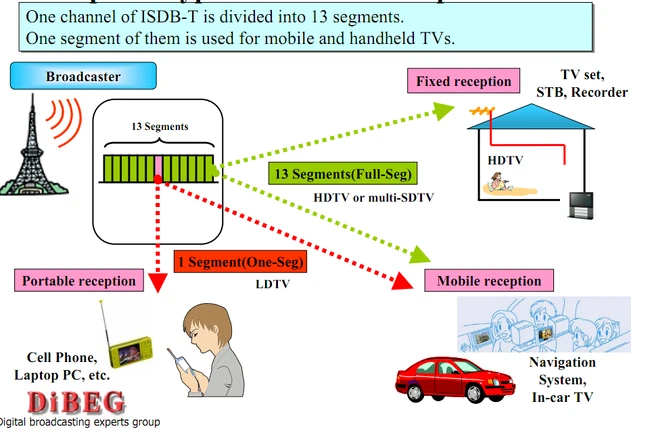
Within the given bitrate determined by the transmission parameters such as bandwidth, code-rate, guard interval, etc. Typically, among the 13 segments, the center segment is used for 1seg (see below) with QPSK modulation. The remaining 12 segments for the HDTV or SDTV payloads for 64QAM modulation. The bitstream of the 12 segments are combined into one transport stream, within which any combination of programs can be carried based on the MPEG-2 transport stream definition.
- ISDB-T transmits a HDTV channel and a mobile TV channel 1seg within one channel. 1seg is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video broadcasting service. Although 1seg is designed for mobile usage, reception is sometimes problematic in moving vehicles. Because of reception on high speed vehicle, UHF transmission is shaded by buildings and hills frequently, but reported well receiving in flat or rural areas.
- ISDB-T provides interactive services with data broadcasting such as Electronic Program Guides. ISDB-T supports internet access as a return channel that works to support the data broadcasting. Internet access is also provided on cellphones.
- ISDB-T provides Single Frequency Network (SFN) and on-channel repeater technology. SFN makes efficient utilization of the frequency resource (spectrum). This is ideal for high urban areas like NCR.
- ISDB-T can be received indoors with a simple indoor antenna.
- ISDB-T provides robustness to multipath interference ("ghosting"), co-channel analog television interference, and electromagnetic interferences that come from motor vehicles and power lines in urban environments.
- ISDB-T is claimed to allow HDTV to be received on moving vehicles at over 100 km/h (this has not yet been proven in real-world operation).
Alert broadcasts
Allows the government or authority configure the emergency warning broadcasting system and send an alert (that can be used to advise Philippine severe weather) to each device in the area ISDB-T signal is present. The alert signal uses some data space in one of the segments of the data stream. ISDB-T turns on all receivers, if turned off, and presents the alert information.[3][4]
An example of such alert is Earthquake Early Warning (EEW), which is well-utilized with alert sound and emergency box superimposed on TV screen at time of the 2011 To-hoku earthquake and tsunami and many aftershocks in several days.
Philippines will implement emergency warning broadcast to households.[5]
Technical specifications
Segment structure
ARIB (Association of Radio Industries and Businesses) has developed a segment structure called BST-OFDM (see figure). ISDB-T divides the frequency band of one channel into thirteen segments. The broadcaster can select which combination of segments to use; this choice of segment structure allows for service flexibility. For example, ISDB-T can transmit both Low Definition TV and High Definition TV using one TV channel.[6] Or change to 3 SDTV, a switch that can be performed at any time. ISDB-T can also change the modulation scheme at the same time.
| s11 | s 9 | s 7 | s 5 | s 3 | s 1 | s 0 | s 2 | s 4 | s 6 | s 8 | s10 | s12 |
The above figure shows the spectrum of 13 segments structure of ISDB-T.
(s0 is generally used for 1seg], s1-s12 are used for HDTV or SDTVs
Summary of ISDB-T
| Transmission channel coding |
Modulation | 64QAM-OFDM, 16QAM-OFDM, QPSK-OFDM, DQPSK-OFDM (Hierarchical transmission) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error correction coding | Inner coding, Convolution 7/8,5/6,3/4,2/3,1/2Outer coding:RS(204,188) | ||
| Guard interval | 1/32,1/16,1/8,1/4 | ||
| Interleaving | Time, Frequency, bit, byte | ||
| Frequency domain multiplexing | BST-OFDM
(Segmented structure OFDM) | ||
| Conditional Access | Multi-2 | ||
| Data broadcasting | ARIB STD-B24 (BML, ECMA script) | ||
| Service information | ARIB STD-B10 | ||
| Multiplexing | MPEG-2 Systems | ||
| Audio coding | MPEG-2 Audio (AAC) | ||
| Video coding | MPEG-2 Video | MPEG-4 AVC /H.264* | |
- H.264 Baseline profile is used in one segment 1seg broadcasting for portables and Mobile phone.
- H.264 High profile is used in ISDB-Tb to high definition broadcasts.
Specification of Japanese terrestrial digital broadcasting using ISDB-T.
| Method | Terrestrial digital broadcasting |
|---|---|
| Frequency band | VHF/UHF, super high band |
| Transmission bit rate | 23 Mbit/s(64QAM) |
| Transmission band width | 5.6 MHz^ |
^ 6 MHz width with 5.572 MHz effective bandwidth and 430 kHz guard band between channels
See Also
- Digital TV: What will happen?
- Digital TV transition: Are you ready to switch to digital?
- Digital TV in the Philippines
- How DTV works
- ISDB-T review in the Philippines
In The News
- ABS-CBN goes to Digital (Taglish)
- GMA-7 can go Digital Anytime
- NTC officially dumped DVB-T2 in favor of ISDB-T
- We're 'turning Japanese' on digital TV platform
References
- ↑ http://www.malaya.com.ph/aug24/busi5.html
- ↑ http://dtvpilipinas.blogspot.com/2011/08/news5-interaksyon-were-turning-japanese.html
- ↑ http://www.gov-online.go.jp/pdf/hlj/20100901/20-21.pdf
- ↑ http://www.mb.com.ph/editorial-the-philippines-goes-digital-broadcasting/
- ↑ http://www.abs-cbnnews.com/business/02/24/11/ntc-wants-digital-tv-service-launched-key-cities-2012
- ↑ http://philippinetelevision.wikia.com/wiki/Digital_TV_Channels_%28NCR%29